In the dynamic world of design, where creativity knows no bounds, prototyping emerges as a beacon of innovation. This humble yet powerful tool bridges the gap between abstract ideas and tangible creations, serving as a cornerstone in the design process. In this article, we delve deep into the emotional significance of prototyping and how it shapes the way we bring visions to life.
Table of Contents
- The Evolution of Design Prototyping
- Empowering Creative Expression
- Enhancing User-Centric Approaches
- Mitigating Costly Errors
- Facilitating Collaborative Design
- Aiding Decision-Making
- Reducing Time-to-Market
- Boosting Stakeholder Confidence
- Fostering Iterative Refinement
- Transforming Concepts into Reality
- Inspiring Innovation
- Creating Emotional Connections
- Adapting to Market Dynamics
- Navigating Complexities
- Future-Proofing Designs
The Evolution of Design Prototyping
Prototyping has come a long way since its inception. It started as rudimentary sketches on paper, gradually transforming into intricate physical models. Today, with the aid of cutting-edge technology, designers can create virtual prototypes that simulate real-world experiences. This evolution has not only revolutionized the design process but also the way we perceive and interact with products.
Empowering Creative Expression
Prototyping serves as a canvas for designers to unleash their creativity. Unlike mere sketches, prototypes offer a tangible manifestation of ideas. The ability to touch, feel, and interact with a prototype sparks new dimensions of creativity, fostering a deeper connection between the designer and the design.
Enhancing User-Centric Approaches
Design is not just about aesthetics; it’s about user experience. Prototyping allows designers to step into the shoes of the end-users, identifying pain points and refining solutions accordingly. This empathetic approach leads to products that are not just visually appealing but also seamlessly functional.
Mitigating Costly Errors
Imagine launching a product only to realize it has a critical flaw that could have been prevented. Prototyping acts as a safety net, revealing design flaws and usability issues early in the process. This prevents costly mistakes, ensuring the final product meets the highest standards of quality.
Facilitating Collaborative Design
Design is often a collaborative effort involving multiple stakeholders. Prototyping provides a tangible platform for communication, enabling designers, engineers, and stakeholders to visualize and align their ideas. This synergy fosters a harmonious design process and reduces misunderstandings.
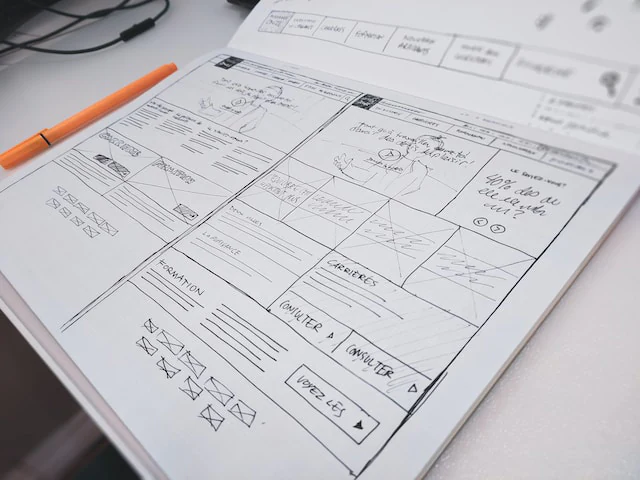
Aiding Decision-Making
Design decisions can be tough, but prototyping makes them easier. By creating physical or virtual representations of design options, designers can assess their feasibility and impact. This informed decision-making streamlines the design process and ensures the chosen path is the most suitable one.
Reducing Time-to-Market
In today’s fast-paced world, time is of the essence. Prototyping expedites the design process by minimizing trial and error. Designers can quickly iterate through multiple concepts, accelerating the journey from ideation to market-ready product.
Boosting Stakeholder Confidence
Stakeholders invest not only money but also their faith in a design project. A well-executed prototype instills confidence by offering a glimpse into the future product. This tangible representation conveys the designer’s dedication and vision, making stakeholders more invested in the project’s success.
Fostering Iterative Refinement
Prototyping promotes a culture of iteration. Designers can continuously refine and enhance their ideas based on real-world testing and feedback. This iterative process ensures that the final design is robust, user-friendly, and aligned with the desired outcomes.
Transforming Concepts into Reality
Design concepts may start as abstract notions, but prototyping brings them one step closer to reality. This transformation is emotionally rewarding for designers as they witness their ideas take shape and substance.
Inspiring Innovation
Prototyping encourages out-of-the-box thinking. By experimenting with various materials, forms, and functionalities, designers push boundaries and explore uncharted territories. This quest for innovation is what drives the design industry forward.
Creating Emotional Connections
Emotion and design go hand in hand. Prototyping enables designers to infuse emotion into their creations. Whether it’s the texture of a material, the curvature of a surface, or the play of light, prototypes evoke emotions that resonate with users on a profound level.
Adapting to Market Dynamics
Markets are dynamic, and trends evolve rapidly. Prototyping equips designers to adapt swiftly to changing market demands. Quick iterations based on real-time feedback ensure that products remain relevant and desirable.
Navigating Complexities
Some designs are inherently complex, involving intricate mechanisms and interactions. Prototyping simplifies these complexities by breaking them down into manageable components. This systematic approach leads to cohesive designs that perform seamlessly.
Future-Proofing Designs
The future is unpredictable, but prototyping helps designers anticipate challenges. By simulating real-world scenarios, designers can identify potential bottlenecks and design solutions that are robust enough to withstand the test of time.
Conclusion
In the realm of design, prototyping is not just a technical step; it’s an emotional journey. It’s about transforming imagination into reality, about feeling the pulse of innovation, and about connecting with users on a profound level. As technology continues to advance, the role of prototyping will only become more pivotal in shaping the way we design, experience, and interact with the world around us.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of prototyping in design?
Prototyping primarily serves to bring design ideas to life in a tangible form for testing and refinement.
How does prototyping contribute to creativity in design?
Prototyping provides a platform for designers to experiment, iterate, and push creative boundaries.
Can prototyping help in reducing design errors?
Absolutely. Prototyping identifies design flaws early, preventing costly errors in the final product.
Is prototyping limited to physical products?
No, prototyping now includes virtual prototypes, simulations, and interactive experiences.
What is the future outlook for design prototyping?
The future holds exciting possibilities with virtual reality, augmented reality, and more immersive prototyping methods on the horizon.